Human-wildlife conflict and coexistence is a shockingly common problem, often with enormous consequences for both individual animals and entire populations.
When human-wildlife conflict comes to mind, you may immediately think of wildlife crime instead - which isn't wrong, since many regions with wildlife crime problems like poaching are also areas where people may frequently deal with human-wildlife conflict, causing the two issues to go hand-in-hand. But human-wildlife conflict is a much broader issue encompassing many ways that human presence and interference can cause problems for us and animals alike. Human-wildlife conflict includes:
- Elephants trampling a farmer's crops, resulting in retaliation
- New real estate developments infringing on ecosystems where predator species live, leading to predators having less territory and less food, which in turn leads to predators attacking domestic animals and livestock
- Freeways dividing the territory of animals like mountain lions, leading to wildlife venturing into neighborhoods or being killed by cars
- Lead bullets used in hunting causing scavengers like condors to die of lead poisoning
These are just a few examples of how humans can negatively impact wildlife, and it's clear to see how many of these scenarios could escalate. Human-wildlife conflict solutions don't just include ways in which we can prevent these issues (for example, through tracking predators, monitoring populations' territories, or building barriers and wildlife crossings monitored by sensors), but also the ways in which we can help people connect with wildlife and care about learning to live alongside them.
If you're interested in solutions that can prevent human-wildlife conflict, join this group and get to know the people who are working to protect and save species around the world!
Header image: Casey Allen on Unsplash
No showcases have been added to this group yet.
- @Kelp
- | Mrs. she her
love whales
- 0 Resources
- 1 Discussions
- 2 Groups
WILDLABS & Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS)
I'm the Bioacoustics Research Analyst at WILDLABS. I'm a marine biologist with particular interest in the acoustics behavior of cetaceans. I'm also a backend web developer, hoping to use technology to improve wildlife conservation efforts.





- 41 Resources
- 38 Discussions
- 33 Groups
R & D Tech | Industrial Designer | Wildlife Management Technology



- 0 Resources
- 93 Discussions
- 6 Groups
- @Agripina
- | Miss
Frankfurt Zoological Society
As a wildlife conservationist, I am deeply committed to nature conservation, community empowerment, and wildlife research in Tanzania. I've actively engaged in community-based projects, passionately advocating for integrating local communities into conservation.
- 3 Resources
- 25 Discussions
- 6 Groups
- @carlybatist
- | she/her
ecoacoustics, biodiversity monitoring, nature tech



- 113 Resources
- 361 Discussions
- 19 Groups
I'm a software developer. I have projects in practical object detection and alerting that is well suited for poacher detection and a Raspberry Pi based sound localizing ARU project



- 0 Resources
- 432 Discussions
- 7 Groups
- @TaliaSpeaker
- | She/her
WILDLABS & World Wide Fund for Nature/ World Wildlife Fund (WWF)
I'm the Executive Manager of WILDLABS at WWF



- 23 Resources
- 64 Discussions
- 31 Groups
- @bluevalhalla
- | he/him
BearID Project & Arm
Developing AI and IoT for wildlife





- 0 Resources
- 55 Discussions
- 8 Groups
- @sam_lima
- | She/her
Postdoctoral Associate studying burrowing owls at the San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance


- 0 Resources
- 6 Discussions
- 5 Groups
Aeracoop & Dronecoria
Computer engineer, Drone Pilot, Seed researcher, Wild Tech Maker





- 3 Resources
- 37 Discussions
- 11 Groups
- 0 Resources
- 0 Discussions
- 10 Groups
- 0 Resources
- 0 Discussions
- 10 Groups
Read our interview with Sandra Maryanne, a young conservation tech innovator raised in Taita, Ivarenyi with first-hand experience on the challenges of human-elephant conflict within her community. To address this, she...
7 August 2023
Human-Wildlife Conflict is a pressing conservation challenge affecting natural ecosystems, biodiversity and local communities across East Africa. This has led to the development and adoption of diverse conservation...
1 August 2023
JICA, Japan’s International Cooperation Agency is seeking a digital partner with a proven track record in conservation technology as we launch a pilot project to test technologies to mitigate human-elephant conflict in...
19 June 2023
In this Conservation Tech Showcase case study from Big Life Foundation, you’ll learn about their successes using EarthRanger and LoRaWAN Smart Parks Solution technologies to monitor wildlife in East Africa.
8 June 2023
Richard Turere from Kitengela, invents flashing lights to mitigate human wildlife conflict. He came up with “Lion Lights,” a system that deters predators such as lions from attacking livestock using flashing lights....
31 May 2023
Are you using or creating tech to protect wildlife? We want to support your organization through two $15,000 grants!
15 May 2023
Quick feature of Virgina Tech project using camera traps and biologgers to track bobcats, collecting data to inform human-wildlife coexistance efforts
26 April 2023
New paper in Trends in Parasitology discusses how acoustic monitoring can be used to assess presence and overlap of host or reservoir species, disease vectors and human activity.
8 March 2023
New article about how climate change and human-wildlife conflict go hand-in-hand. Would be interesting to hear from our climate change and HWC groups about how climate scientists and community members who are innovating...
1 March 2023
Article
Assessing the Efficacy of a Novel Olfactory Approach to Mitigating Elephant Crop Raiding in Uganda and Kenya
24 February 2023
Scholarships available for training courses focussing on nature restoration in East Africa
21 February 2023
Technology to End the Sixth Mass Extinction. Salary: $104k-144K; Location: Washington DC or Seattle WA, potential hybrid; 5+ years of Full stack development experience; Deadline March 15th - view post for full job...
10 February 2023
October 2025
event
July 2025
32 Products
3 R&D Projects
42 Organisations
Recently updated products
Recently updated R&D Projects
Recently updated organisations
| Description | Activity | Replies | Groups | Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hello WILDLABS! As humbled and grateful recipients of a 2025 WILDLABS Award, we are excited to introduce our project to the community. Our... |
|
Human-Wildlife Coexistence, East Africa Community | 2 months 2 weeks ago | |
| Hi. Currently working on a project on an island where recreational activity is impacting breeding seabirds. Looking for AI solutions for... |
|
Human-Wildlife Coexistence | 2 months 3 weeks ago | |
| Great dear Travis,This is a great news and an opportunity to me and my local bee keepers. It really sounds very helpful.Here is my contacts:Email: muganyizi@pales.or.tz ... |
|
Climate Change, Conservation Tech Training and Education, East Africa Community, Funding and Finance, Human-Wildlife Coexistence, Wildlife Crime | 4 months ago | |
| Good morning JocelynThank you very much for your comment, this is proving to be very useful advice and thank you so much for setting me on the right path!! This is very exciting!!... |
|
Animal Movement, Citizen Science, Human-Wildlife Coexistence, Marine Conservation, Drones, Community Base, Geospatial | 4 months 2 weeks ago | |
| Hi Nikita, If you haven't already, I'd recommend reaching out to the folks at the Cornell Ornithology lab. They're really glued into all things bird. In particular, I... |
|
Animal Movement, Drones, Emerging Tech, Human-Wildlife Coexistence | 4 months 3 weeks ago | |
| I'm sure others here can comment better than I on models for classifying animal sounds, but from an ML pint of view, a key concern is getting enough data. 10 recordings does not... |
|
AI for Conservation, Animal Movement, Human-Wildlife Coexistence | 4 months 3 weeks ago | |
| Love it! I have a few ideas. |
+15
|
Conservation Tech Training and Education, Funding and Finance, Human-Wildlife Coexistence | 6 months ago | |
| Hello everyone. My name is Bilal. I recently graduated with a degree in bioengineering and hold a bachelor's degree in computer science,... |
|
AI for Conservation, Animal Movement, Human-Wildlife Coexistence, Marine Conservation | 6 months 4 weeks ago | |
| @HeinrichS there’s still time for you or anyone else to make a funding submission to the wildlabs 2025 grants ❤️❤️❤️I haven't applied for wildlabs funding, but I would love for... |
|
Human-Wildlife Coexistence, AI for Conservation, Camera Traps, Emerging Tech | 7 months ago | |
| Hats off to your team for this absolute game-changing technology! We rescue stray and wild animals in Taiwan, and the bulk of our work is saving animals maimed by wire snares... |
+37
|
AI for Conservation, Drones, Emerging Tech, Human-Wildlife Coexistence, Wildlife Crime | 8 months 3 weeks ago | |
| There's quite a few diy or prototype solutions described online and in literature - but it seems none of these have made it to market yet as generally available fully usable... |
|
AI for Conservation, Camera Traps, Human-Wildlife Coexistence, Sensors | 8 months 3 weeks ago | |
| Oops, sorry about that. I wrote a reply a few weeks ago, and I am pretty sure I clicked the button, but apparently something went wrong. So, another attemptThank you for your... |
|
Community Base, Conservation Tech Training and Education, East Africa Community, Funding and Finance, Human-Wildlife Coexistence, Latin America Community | 9 months 1 week ago |
Updates on Mole-Rat Mystery Drone Project
10 June 2025 10:21am
12 June 2025 11:33am
Thank you Elsa :)
14 August 2025 6:07am
want to join 2025 contest for humpback whale photos in Juneo Alaska of Kelp
Women Conserving Southern Africa
16 July 2025 10:38am
24 July 2025 9:01pm
Thanks for sharing this, Emily! Feel free to also add this as an event on WILDLABS so it appears on our community calendar.
25 July 2025 8:10am
Thanks for that Alex, I've added the event!
14 August 2025 3:29am
This is wonderful, thanks for sharing!
Seeking Connections with Chile’s Wildlife Conservation
11 August 2025 6:28pm
Zimbabwe Shines: 5 Key Takeaways from Ramsar COP15
10 August 2025 11:56pm
Apis Nomadica Labs: Mobile Bee-Search for the Future of Food & Medicine
7 August 2025 8:23am
How do you tackle the anomalous data during the COVID period when doing analysis?
21 July 2025 8:55am
25 July 2025 3:06pm
To clarify, are you talking about a model that carries out automated detection of vocalizations? or a model that detects specific patterns of behavior/movement? I would suspect that the former is not something that may be impacted while training as the fundamental vocalizations/input is not going to change drastically (although see Derryberry et al., where they show variation in spectral characteristics of sparrows at short distance pre and post-covid lockdowns).
28 July 2025 6:14pm
I'm specifically referring to movement of animals affected by anthropogenic factors. My question has nothing to do with vocalisations.
Humans were essentially removed from large sections of the world during covid and that surely had some effects on wildlife movements, or at least I am assuming it did. But that would not be the regular "trend". If I try to predict the movement of a species over an area frequented by humans, that surely comes into the picture - and so does their absence.
My question is very specific to dealing with data that has absence (or limited interference) of humans during the covid period in all habitats.
1 August 2025 10:24pm
You could just throw out that data, but I think you'd be doing yourself a disservice and missing out on some interesting insights. Are you training the AI with just pre-COVID animal movement data or are you including context on anthropogenic factors as well? Not sure if you are looking at an area that has available visitor/human population data, but if you include that with animal movement data across all years it should net out in the end.
July Geospatial Café Q&A
25 July 2025 5:53pm
25 July 2025 5:57pm
- I have question. As Dr Muhammad Rais mentioned ArcGis and QGIS for spatial analysis, map creating etc. If we can also done these analysis with python such as spatial analysis etc and sp, sf function in R for spatial analysis. So why everyone recommend ArcGis. And 2nd question about map of life. Can we download data from that for spatial analysis or habitat modeling.
25 July 2025 5:58pm
- Lovely to hear your work curating the Map of life @eliseb227. When uploading shapefiles, is it accurate to create a list of exhaustive species identified within a landscape which could see incidents of conflict. can we include community knowledge in this list?
28 July 2025 7:43am
Good question. Not sure everyone recommends ArcGIS anymore, but it is commonly used as a desktop GIS. However, it's not free. QGIS, R, and various Python packages are free. But you just need to know how to code to use them. In fact, using R and Python is often cleaner, faster, and puts you in touch with the data and how it's analyzed, much better than the 'clicky clicky' used in desktop packages. Most will use both desktop and code in the workflows. Among others, please see geemap.org, leafmap.org, and FOS geospatial tools for resources to get started and for a deeper dive. Additionally, please see the articles and discussions in this group.
WILDLABS AWARDS 2024 - Innovative Sensor Technologies for Sustainable Coexistence: Advancing Crocodilian Conservation and Ecosystem Monitoring in Costa Rica
11 July 2024 11:30pm
14 December 2024 6:41pm
¡Muchas gracias @vanereyes, apreciamos su apoyo!
4 February 2025 11:44am
Super interesting! I'm currently developing sensor accelerometers for fence perimeters in wildlife conservation centres. I think this is a really cool application of accelerometers; I would love to know how the sensor which you developed for part 3 looked like, or what type of software/machine learning methods you've used? Currently my design is a cased raspberry pi pico, combined with an accelerometer and ml decision trees in order to create a low-cost design. Perhaps there is something to be learnt from this project as well :)
4 February 2025 2:45pm
Wonderful video! Really impressive :)
Foxlights predator deterrant
24 November 2015 6:53pm
23 March 2017 12:24pm
Thanks for the reply. I will write to the contact because of the doubts.
24 March 2017 8:22pm
Personally, I'd order a few of the $10 radios from eBay and see how they work. They are cheap enough that if they don't work out, you wouldn't be out much money.
For $27, you could try one of these which is rated Waterproof Level IPX3; it can be used during rainy weather.
From my brief search, I think you are going to have a tough time finding something solar, waterproof, and inexpensive. But do let us know what you turn up!
18 July 2025 9:22am
Really appreciate this discussion and the collective interest in humane, non-lethal deterrent solutions.
We at Katidhan, based in India, have been working on a similar innovation called Parabraksh — a solar-powered smart deterrent that uses randomized light patterns to simulate the presence of a threat (like eye contact or motion). It’s specifically designed for deterring elephants, wild boars, leopards, tigers, and other wild animals that cause crop loss or endanger human settlements.
Inspired by the efforts of Lion Lights and Foxlights, we focused on building a solution that’s cost-effective, rugged, and adaptable to diverse geographies. Parabraksh is certified by a government agri-university and has been deployed in over 5,000 installations across India, including projects with state forest departments.
We understand the concerns around animal habituation, and Parabraksh addresses this with a dynamic light logic that changes patterns and behavior unpredictably. When combined with smart field practices and periodic repositioning, the deterrent effect has remained effective across long deployment cycles.
If anyone is interested in trying or procuring the system, feel free to reach out to me directly at previn@katidhan.com. We’re happy to collaborate or share insights.
Warm regards,
Previn Jacob
Katidhan | www.katidhan.com
CSS Asian elephant rapid response grant
4 July 2025 9:31pm
Opportunity to participate in study on what evidence you trust in conservation
24 June 2025 1:14pm
Field testing the PolarBearWatchdog!
23 June 2025 12:24am
23 June 2025 1:23pm
Looking forward to capturing the first polar bear. On film of course.
New Group Proposal: Systems Builders & PACIM Designers
18 June 2025 2:52pm
19 June 2025 9:08am
Hi Chad,
Thanks for the text. As I read it, PACIMs play a role in something else/bigger, but it doesn't explain what PACIMs are or what they look like. Now I've re-read your original post, I'm thinking, maybe I do understand, but then I feel the concept is too big ( an entire system can be part of a PACIM ? ) to get going within a WildLabs group. And you want to develop 10 PACIMS within a year through this group? Don't get me wrong, I am all for some systems change, but perhaps you're aiming too high.
19 June 2025 12:19pm
Hello again sir - PACIMs really mean 'projects' is the way I see it. Each part of the acronym can be seen as a project (if you have an assignment to do, you have a project really).
As for your query on 10 projects in 'this' group - I should ask for clarification if you mean particularly acoustics or in any group (I see now this is the acoustics thread after I selected all the groups for this post). If you are asking on acoustics, you're right - I am unsure on 10 as I am not too keen on acoustics yet. If you are asking 10 projects as a whole like 10 projects in the funding and finance group - I believe 10 to be a very reasonable number. Our projects we have co-created are for the most part replicable, rapidly deployable, quickly scalable, fundable through blended finance and more.
Thank you again for the feedback.
19 June 2025 1:43pm
Thank you for your reply, Chad
I meant 10 as a whole, indeed. Perhaps you see your post in one group, but since it is tagged for all groups, I assumed you meant 10 in total.
In your first post you explain PACIM stands for "Projects, Assignments, Campaigns, Initiatives, Movements, and Systems", so I understood it as more than just projects. Obviously, many things can be packed into a project or called a project, but then, what does it mean that 'Projects' is part of the list?
Well, if you think 10 projects is doable, then don't let me stop you.
How drones, AI & Open Source Software are being used to combat Alien Invasive Plants in South Africa
2 June 2025 10:08am
7 June 2025 9:36pm
Hi Ginevra, thank you! Its such a huge advantage to have tech tools available to us in conservation. Not just from an analysis point of view but also from a practical application view😊
17 June 2025 1:26am
Aloha, this is a great project. Thanks for sharing. I have been looking for ideas to integrate machine learning with some of the conservation work we are engaed in here on Kauai. Thank you
17 June 2025 11:00am
Thank you for your comment Chris! Using these tools has made a huge difference in the way we can monitor and manage Invasive Alien Vegetation. I hope you are able to integrate similar systems with your projects there. If you need any help, feel free to reach out!
Apply for Free Access to Nature FIRST Conference (innovative solutions for biodiversity monitoring and human-wildlife coexistence)
22 May 2025 2:37pm
28 May 2025 4:20pm
Nice!
Thought I'd mention that Wildlife Security Innovations will have a booth there, demonstrating our new multi-camera, local AI camera trap that supports miniature high resolution thermal modules. I will be bringing these along.
31 May 2025 4:21pm
Hi
This is great!
So just to double check - there is no way to join online? I would love to be part of this conference.
Thanks, Els van Lavieren
WILDLABS AWARDS 2025 - Ambiance: Leveraging Fear to Mitigate Human-Wildlife Conflict
25 May 2025 10:38pm
Automated Image analysis
18 May 2025 5:10pm
Boombox Workshop at ICCB 2025
16 May 2025 8:18am
Technology in Wildlife Welfare Workshop (in-person, UK)
6 May 2025 7:46pm
Post-Doctoral Research Fellow/ Project Manager, University of St. Andrews, UK
2 May 2025 4:31pm
Connecting the Dots: Integrating Animal Movement Data into Global Conservation Frameworks
 Lacey Hughey
and 3 more
Lacey Hughey
and 3 more
30 April 2025 1:38am
FROM VULNERABILITY TO SECURITY: INSPIRING COEXISTENCE THROUGH A RESILIENT BOMA
17 April 2025 8:41pm
Beekeeping training center/field school
3 April 2025 10:38am
4 April 2025 2:16pm
Thanks.
Any time you meet someone with internet to invest in the beekeeping industry. Kindly remember my name.
8 April 2025 9:17am
Hi, I'm really interested in your project. If you're open to it, I’d be happy to build and send you a couple of data logger units — free of charge — to help monitor temperature, humidity, pressure, and possibly hive weight using a load cell. I’m also considering adding a simple bee traffic sensor to track how often bees enter and leave the hive. This could help reveal patterns related to foraging behavior or colony stress.
It would also be an interesting use case for using LoRaWAN to send node data to a central gateway. The data could be exported in line protocol format so you can easily import it into InfluxDB or another dashboarding tool if you'd like to visualize it.
I’m quite busy with other projects, but I’d be happy to throw something together to get you started, and I’ll include the source code in case you'd like to modify or expand it in the future. Let me know if this sounds helpful — I'd love to support your work.
Best regards, Travis
8 April 2025 2:36pm
Great dear Travis,
This is a great news and an opportunity to me and my local bee keepers. It really sounds very helpful.
Here is my contacts:
Email: muganyizi@pales.or.tz
Mobile WhatsApp: +255686 821 070.
Kindly spare a time slot so that we dive into details of this for your support and collaboration.
Free Webinar by Nature FIRST: Bridging Ecology and ESG – Smarter Decisions with Knowledge Graphs
2 April 2025 10:59am
Mole-Rat Mystery. Can anyone help?
19 March 2025 3:25pm
20 March 2025 4:17pm
Hi Sean! I love that you are naturally curious and are pursuing really cool projects in your free time. I know absolutely nothing about cape dune mole rats (in fact, never heard of them prior to this post, but I will confess I was interested in the concept of a mole-rat mystery), but I did have some thoughts about where you might find more information-
It seems like the types of questions you are asking are pretty specific and niche. My first thought on how to find someone with expertise in these specific rodents was to go to their iNat page- there you can see the top observer and top identifier. Both individuals are active researchers, so I think reaching out to them on iNat or finding their e-mails from their respective organizations' sites might be a good way to get in touch.
I also did a quick search in Google Scholar in which I typed in only the scientific name and hit go. The two publications linked above caught my eye as potentially helpful in your search- particularly the first one. They excavated burrows and noted things like home range size, that males have more burrows than females, etc. I didn't go much beyond the abstracts but these seem like they might get you on the right tracks!
Happy ratting!
25 March 2025 8:36am
Good morning Vance
Thank you very much! I am looking into some papers that I was kindly directed to by Jocelyn Stalker ( her comment below) and am looking for ways to establish population dynamics just by looking at the mounds. Once I have figured this part out I should be able to correlate the information to the drone data. The Ground Sampling Distance (GSD) for this project is very small, 1.3cm per pixel. This has proven to be very useful because I am able to use the very fine 3D models to run change detections that pick up new heaps and vegetation reductions (which may be due to feeding) on a weekly basis. It helps not only visualise but also quantify where the most activity has occurred. I will keep you posted!
25 March 2025 8:47am
Good morning Jocelyn
Thank you very much for your comment, this is proving to be very useful advice and thank you so much for setting me on the right path!! This is very exciting!!
They are the most extra ordinary little creatures and as I don't know much about them either, I thought I'd try learn as much as I can (not just through literature, but through my own observations as well). I walk past these mounds daily and am always intrigued when I see more mounds and really enjoy watching them actively push the dune sand up to the surface (you don't see the wee fellas but you can watch the sand move as they burrow away). One afternoon while flying my drone (I was quantifying the changes in sediment deposition and erosion volumes in the estuary after a flood that was soon followed by a super high tide), I had a heap between my legs and all of a sardine it starts moving! So that sparked my curiosity even further.
I will keep you posted on my findings and thank you again for the papers and the direction! It is greatly appreciated!!
Drone for Studying Migratory Birds - Research Input
9 October 2024 4:55pm
18 February 2025 10:42pm
Hi! I would be interested to learn more about your project. Would you send me your contact email? Mine is melisa.simic@nuveen.com - We are infrastructure investors globally working with both clean energy and diversified infra assets.
Thanks, Melisa
24 February 2025 4:24am
Hi Melisa,
I have emailed you the project idea. Hope to hear from you soon. My email address is: Geometry Dash Lite jonathonreese0924@gmail.com
21 March 2025 3:25pm
Hi Nikita,
If you haven't already, I'd recommend reaching out to the folks at the Cornell Ornithology lab. They're really glued into all things bird. In particular, I remember seeing a presentation years ago about their project birdcasting, which was measuring bird migration via radar. One of their next steps was to connect small scale behavior to large scale movement data, and it sounds like your drone project could help fill that gap.
Cheers,
Brandon
Subject: “Baa-bridge” – AI Sheep Stress Reduction, Seeking Genius Input!
20 February 2025 9:55pm
21 March 2025 12:18pm
I'm sure others here can comment better than I on models for classifying animal sounds, but from an ML pint of view, a key concern is getting enough data. 10 recordings does not sound like a lot (although how long are they?) and 1000 epochs does sound like a lot. It is very possible that your model is just learning to memorize the inputs, and that it will generalise poorly.
Nature FIRST Conference: Innovation and Collaboration in Conservation
11 March 2025 9:39am
Arctic Community Wildlife Grants Program
7 March 2025 3:59pm
MargoTV - new wildlife tech youtube series and subsidized conservation products!
9 January 2025 12:17am
12 February 2025 7:28pm
That’s great! Definitely interested!
Think in terms of 10W continuously.
13 February 2025 7:43am
I'm looking forward to the cool Margo TV we are going to see when we get some AI bear monitoring going in Canada with Margo supplies :) That's going to be awesome.
Here is an image of a bear from last night in the Scandinavian zoo in Denmark. The system triggered on the bear even though it is very dark and this is a digital zoom on a wide angle fixed camera. Despite being very fuzzy we are able to get triggers on these ones due to the use of multiple mitigation techniques so we get long distance, high sensitivity and low false positives. This one for example was checked with multiple successive frames and multiple AI models before calling it a bear.
This is without thermal. But with added thermal and models trained on thermal images the heat signature will effectively be taken up in the model I'm expecting. This would mean that in effect you can tolerate a lower confidence level but it would after all be a living thing as well.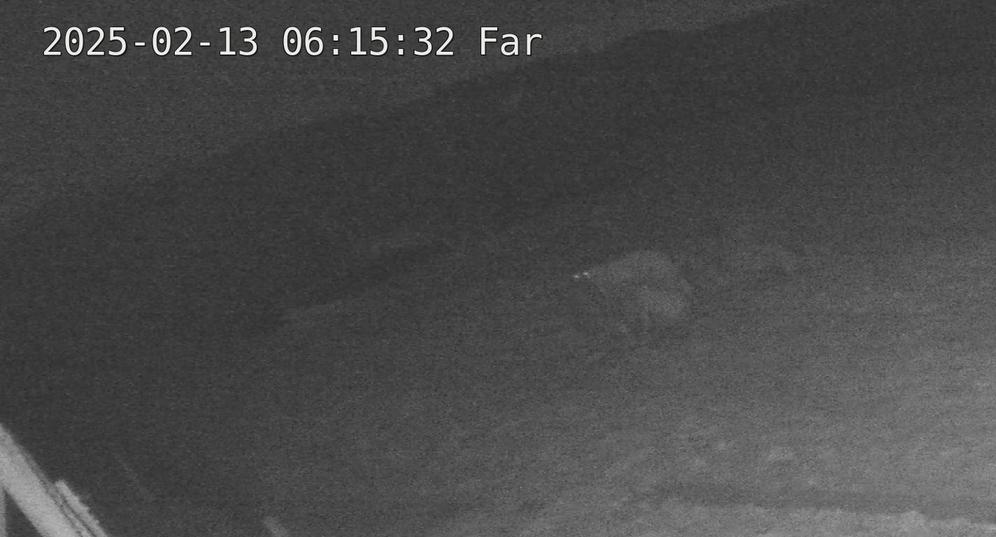
This trigger event for this event was even less clear, but you can still just make out two eyes, and bear in mind (excuse the pun), the actual view from this camera is even wider and the bear further away in a sense as this is a dynamic zoom.
13 February 2025 7:49pm
Love it! I have a few ideas.








































































10 June 2025 6:04pm
Such a great case study!!